TPU 3D Printing, What you need to know
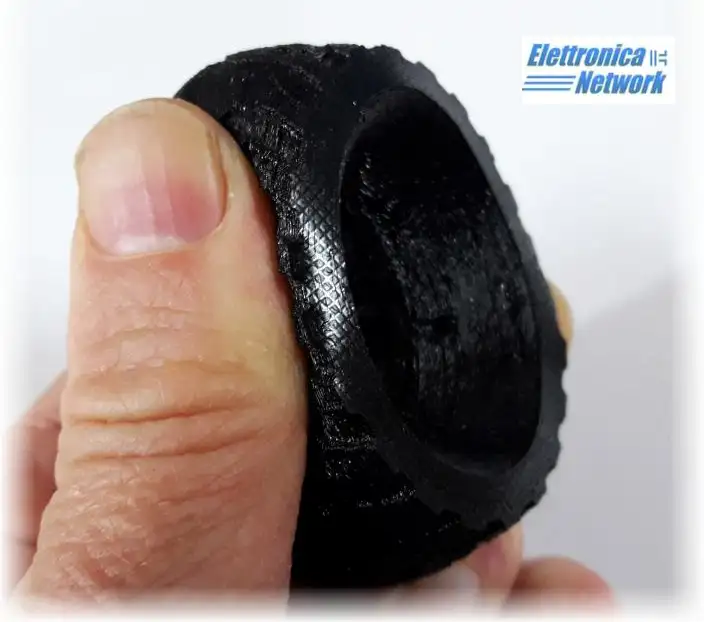

Cos'è il TPU?
Il TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane or Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is an elastomeric thermoplastic polymer belonging to the polyurethane family.
TPU is known for its flexibility, elasticity and tensile strength, Important characteristics that make it a widespread material and also widely used in 3D printing for the production of flexible parts, resistant to thermal and mechanical stress
TPU is a thermoplastic material, which means it can be melted and printed in with 3D printers at high temperatures.
Due to its high elasticity, TPU is used for the production of parts that require some flexibility, like the soles of shoes, Cable sheaths, Enclosures for electronic devices, hoses and much more.
TPU also has good resistance to chemicals and abrasion, making it an ideal material for industrial applications. In addition, TPU is available in different hardnesses called “Shore”, which means it can be used for the production of parts with different hardness and flexibility properties.
How TPU is Made?
TPU is produced through a chemical reaction between an isocyanate and a polyol in the presence of a catalyst. During this reaction, The isocyanate and hydroxyl groups combine to form urethane bonds, creating an elastomeric thermoplastic polymer.
There are several variants of TPU, depending on the specific types of isocyanates and polyols used in production. Generally, the polyols used in the production of TPU are polyesters or polyether, while isocyanates are usually of the aliphatic or aromatic type.
The production process of TPU is very similar to that of the production of rigid polyurethanes, but with a few key differences, such as the use of low molecular weight polyols and low reactivity isocyanates, which makes it possible to obtain an elastomeric material.
Once produced, TPU can be used for a wide range of applications due to its flexibility properties, elasticity, Abrasion and tensile strength.
What are the Properties and Characteristics of TPU?
TPU has numerous properties and characteristics that make it a popular material for a wide range of applications.
Here are some of its main properties and characteristics:
1. Flexibility and elasticity: TPU is known for its high flexibility and elasticity, making it ideal for producing parts that require some flexibility, like the soles of shoes, Hoses and cable sheaths.
2. Tensile strength: TPU has good tensile strength, making it a strong and durable material.
3. Abrasion resistance: TPU is abrasion resistant, making it ideal for industrial applications that require some wear resistance.
4. Chemical resistance: TPU is resistant to chemical agents, making it an ideal material for applications where some chemical resistance is needed.
5. Good adhesion: TPU has good adhesion to other materials, making it ideal for manufacturing composite parts.
6. Variable hardness: TPU is available in different Shore hardnesses, which means it can be used for the production of parts with different hardness and flexibility properties.
7. Ease of processing: TPU is easy to work with and can be 3D printed, thermoformed, Laminated and glued.
Generally, TPU is a versatile and durable material that is used in a wide range of applications, from shoe soles to cable sheaths, up to industrial parts and medical applications.
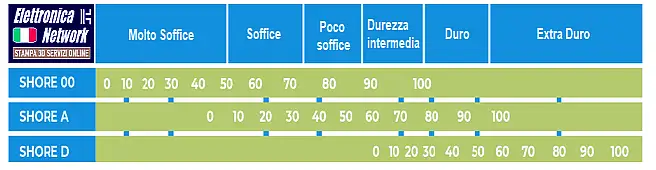
Table in "SHORE" on the Degree of Hardness of TPU
How to 3D Print TPU?
To 3D print with TPU, You can try following these steps:
Prepare your 3D model: use 3D modeling software to create or download a 3D model you want to print.
Configure your 3D printer: Make sure your printer is properly configured to print with TPU. This means checking that the temperature and print speed are set correctly for this material.
The printing temperature of the TPU depends on the type of 3D printer you are using and the specific printing settings you have selected, but in general, TPU requires a relatively low melting temperature compared to other 3D printing materials.
Generally, It is recommended to use an extrusion temperature between 200 and 230 degrees Celsius for TPU. However, It's important to run a series of print tests to find the best temperature settings for your 3D printer and TPU filament. This way you can achieve the best possible print quality with your material of choice.
In addition, it is important to note that some 3D printers require slightly different extrusion temperatures for TPU. Always be sure to consult the manufacturer's instructions for your 3D printer and TPU filament to ensure a high-quality print.
Regarding the print speed for TPU, to obtain the best quality, it is recommended to use a print speed between 20 and 40 mm/s.
However, it's important to note that the print speed also depends on the type of 3D printer you're using and the other print settings you've selected.
TPU typically requires a slower print speed than other 3D printing materials, As too fast a print speed can cause issues such as low adhesion to the print bed, excessive heat build-up and excessive deformation of the material during printing.
To achieve the best print quality with TPU, We recommend running a series of print tests to find the ideal speed settings for your 3D printer and TPU filament. This way you can achieve the best possible print quality with your material of choice.
You can now set up your 3D printer to print TPU, then install the filament in your 3D printer, and possibly also prepare the printing platform with an adhesive suitable for your bed which generally for optimal adhesion will have to be preheated to a temperature of about 75-80 degrees Celsius.
Once you have applied the correct settings for 3D printing the TPU, Be sure to monitor the print closely to avoid issues such as uneven adhesion to the print bed or excessive heat build-up.
Remove the print: Once the print is complete, wait for the plate to cool completely and carefully remove your 3D object from the printing platform.
Clean your 3D printer after each print to ensure it doesn't deteriorate and is ready for the next time you want to print with TPU.
Remember that 3D printing with TPU requires some specific precautions, such as using a direct extrusion printhead, if necessary, it is necessary to check whether it is also necessary to use printing supports capable of supporting the TPU when printing significant overhangs.
Always follow the instructions of your 3D printer manufacturer and in particular make sure to apply the specifications for 3D printing the TPU filament used. to always guarantee a high quality result.
What can be printed with TPU?
TPU is a flexible and durable elastomeric material, making it ideal for producing parts that require some flexibility, Abrasion and tensile strength.
Here are some of the things you can 3D print with TPU:
1. Shoe soles: TPU is often used for the production of shoe soles, thanks to its flexibility and abrasion resistance.
2. Hoses: TPU is used for the production of flexible hoses, such as those used in water or air management systems.
3. Cable sheaths: TPU is often used for the production of cable sheaths, thanks to its flexibility and elasticity.
4. Enclosures for electronic devices: TPU is used for the production of electronic device enclosures, as a smartphone or tablet, thanks to its resistance to falls.
5. Sports Equipment Protectors: TPU is used for the production of protections for sports equipment, as helmets, Knee pads, elbow pads, thanks to its flexibility and impact resistance.
6. Prototypes: TPU is used for prototype production, thanks to its ease of processing and flexibility.
7. Bushings to absorb shock and vibration in motor vehicles, in particular, TPU is also used in the various components for car suspensions as shock absorbers, Arms, limit switch etc.
Generally, TPU is used for the production of parts that require some flexibility, Abrasion and tensile strength, making it an ideal material for a wide range of applications.
